Introduction
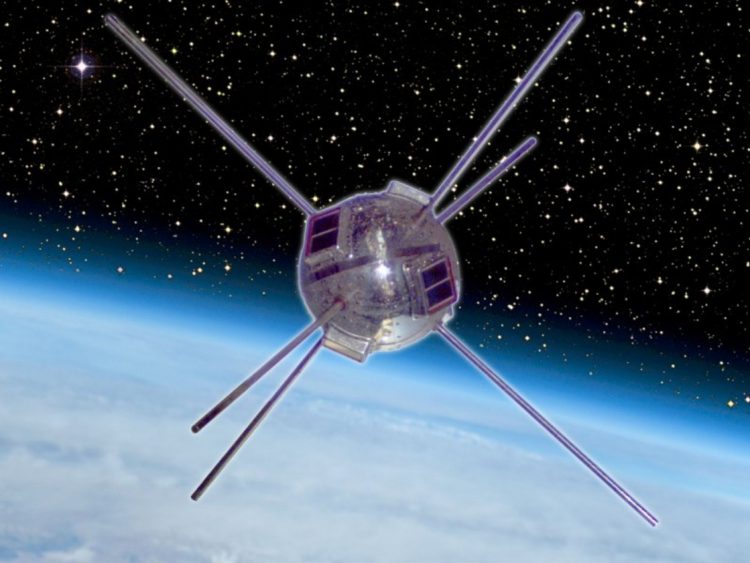
Vanguard 1, also known as the Vanguard Satellite, holds a special place in the history of space exploration. Launched by the United States in 1958, Vanguard 1 was the fourth artificial satellite to be sent into space and the second successful one. While not as well-known as the famous Sputnik 1, Vanguard 1 played a significant role in advancing our understanding of space and has several fascinating lesser-known facts associated with it.
1. The Oldest Human-Made Satellite
Vanguard 1 holds the distinction of being the oldest human-made satellite that is still in orbit. Over six decades have passed since its launch, yet Vanguard 1 continues to orbit Earth, making it a testament to the durability and reliability of early space technology.
2. International Geophysical Year
Vanguard 1 was launched as a part of the International Geophysical Year (IGY) program. The IGY was a global scientific initiative that aimed to promote international cooperation and advance our knowledge of Earth and space sciences. Vanguard 1 was a symbol of the United States’ contribution to this important scientific endeavor.
3. First Solar-Powered Satellite
One of the notable features of Vanguard 1 was that it was the first satellite to be powered by solar cells. It used sun-powered photovoltaic cells to generate electricity, enabling it to operate for an extended duration. This breakthrough paved the way for future satellites to rely on solar power, reducing the need for heavy batteries or fuel.
4. Accurate Spherical Shape
Vanguard 1 was designed to have a nearly perfect spherical shape. It was crucial for the satellite to have a precise shape as it helped scientists accurately measure the atmospheric drag on the satellite. Vanguard 1’s elegant design and shape contributed to its long life in orbit.
5. Contributed to Research on Earth’s Shape
One of Vanguard 1’s primary missions was to aid research on Earth’s shape. Scientists used the satellite’s precise orbit data to calculate the Earth’s polar flattening. The data gathered by Vanguard 1 significantly improved our understanding of the Earth’s shape and provided crucial insights into geodesy and gravity field measurements.
6. Silent But Not Forgotten
Although Vanguard 1 stopped transmitting signals in 1964, it remains an active satellite in orbit. Decades after its communication ceased, Vanguard 1 still serves as a silent observer of space. Its significance in the history of space exploration is acknowledged by the scientific community.
Conclusion
Vanguard 1, the lesser-known satellite, played a vital role in advancing our knowledge of space and Earth. With its long-lasting stay in orbit, it continues to inspire and intrigue scientists and space enthusiasts alike. As we explore the vastness of the cosmos, let’s not forget the contributions made by Vanguard 1 and its remarkable lineage in shaping our understanding of the universe.